Imagine stepping into a room where the light adjusts to your mood or what you need to do. This isn’t just a dream with LED dimming—it’s real and simple.
Dimmable LED lights can warm up a restaurant for a cozy dinner or brighten an office for work, making places more welcoming and helping people do better. Plus, using dimmable LEDs wisely can cut down on energy use, like dimming lights in an empty parking area at night to save power but still keep it safe.
With the right dimmer switch, managing the brightness of LED bulbs or light fixtures becomes a breeze, allowing for a smooth transition from bright to soft light.
This control can significantly enhance the ambiance in any setting, from creating a relaxing environment at home to setting the perfect scene in commercial spaces. It’s not just about setting the right mood; it’s also about being smart with energy.
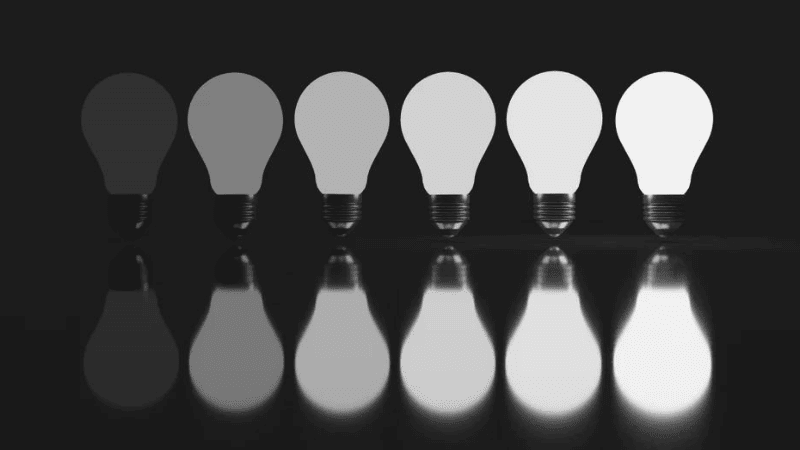

Whether it’s a bustling office space needing clear, focused light or a quiet corner designed for relaxation, LED dimming technology enables precise control over the lighting atmosphere.
This is crucial for achieving the best lighting design that matches the functional and aesthetic needs of any environment. Plus, it’s an eco-friendly choice. Dimming LEDs when full brightness isn’t necessary not only extends the life of the LEDs but also contributes to energy savings, making it a win-win for both your space and the planet.
Types of LED Dimming
LED dimming technologies vary, each with its own method of controlling the brightness of LED lights. Here are some common types:
| Dimming Technology | Description | Compatibility | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leading Edge | Cuts AC voltage at the start of each cycle. Common with incandescent bulbs. | Less compatible with LED lights. | Less expensive. | May cause noise; less smooth dimming. |
| Trailing Edge | Cuts voltage at the end of the cycle. Better suited for LED lighting. | More compatible with LED lights. | Smoother dimming; less noise. | More expensive. |
| PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) | Controls brightness by turning LEDs on and off rapidly. | High compatibility with LEDs. | Efficient; maintains color quality. | Requires specific control systems. |
| 0-10V Dimming | Uses a low voltage signal to control brightness. | Common in commercial and industrial settings. | Straightforward; reliable. | Requires additional low-voltage wiring. |
| DALI (Digital Addressable Lighting Interface) | Provides digital control over dimming, allowing individual light control. | Flexible for commercial and sophisticated residential systems. | Precise control; programmable. | More complex installation; higher cost. |
| DMX (Digital Multiplex) | Developed for theatrical lighting, controls multiple channels for dynamic displays. | Suitable for stage and complex lighting installations. | Detailed control over lighting effects. | Overly complex for simple dimming needs. |
1. Phase-Cut Dimming
This is divided into two categories:
- Leading Edge: Commonly used with incandescent bulbs, leading edge dimmers work by cutting the AC voltage at the start of each cycle. They are less expensive but might not always be compatible with LED lights due to the different electrical characteristics.
- Trailing Edge: These are more compatible with LED lighting, cutting the voltage at the end of the cycle. Trailing edge dimmers are known for smoother dimming and less noise but tend to be more expensive.
2. PWM (Pulse Width Modulation)
PWM dimming controls brightness by turning the LED on and off at a rapid pace—so fast that the human eye can’t detect the flickering. The perceived brightness is determined by the ratio of the on/off cycle. This method is efficient and maintains the color quality of the LEDs.
3. 0-10V Dimming
In this method, a low voltage (0-10 volts) is used to control the brightness of the light. It’s straightforward and reliable and often used in commercial and industrial settings. The dimming level is proportional to the voltage applied, where 0V is fully dimmed, and 10V is the brightest.
4. DALI (Digital Addressable Lighting Interface)
DALI provides digital control over dimming. Each light fixture can be individually addressed, allowing for sophisticated lighting schemes and precise control over brightness levels. It’s highly flexible and used in both commercial and sophisticated residential lighting systems.
5. DMX (Digital Multiplex)
Originally developed for theatrical lighting, DMX is used for controlling stage lights and effects, including LEDs. It allows for detailed control over multiple channels, making it suitable for dynamic lighting displays and complex installations.
Ask For Free Quote
Let us Respond Promptly for your Needs :)
How Does LED Dimming Work?
LED dimming is a cool trick that makes your lights brighter or dimmer without using extra energy. It’s done with something called Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), which is a fancy way of saying the lights flicker on and off super fast – so fast that we can’t even see it happening.
Think of it like blinking your eyes. If you blink really fast, you’ll see less light. But if you blink slowly, you’ll see more light. That’s how PWM works with LEDs. When the LED is on more than off, your room is bright. When it’s off more than on, your room gets dimmer.
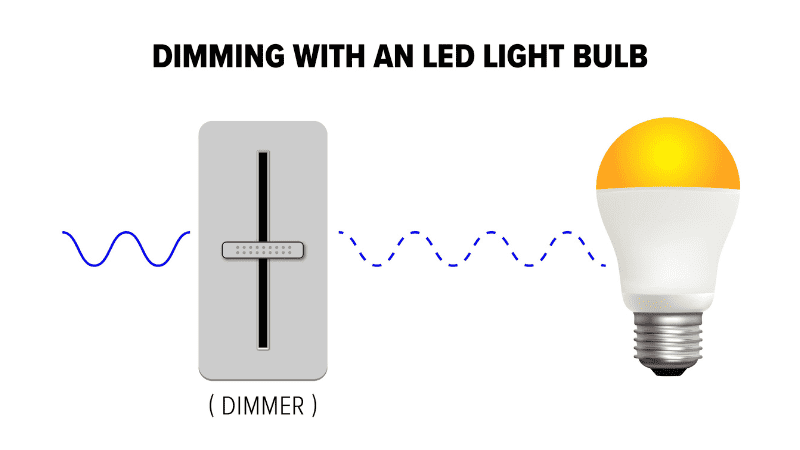
So, if you’re reading and need more light, the LED stays on longer. But for movie time, when you want it dimmer, the LED stays off more. This way, you get to choose how bright your room is, all without changing the light color or wasting energy.
Why Do We Need Dimmable LED Lights
Having dimmable LED lights in your space comes with a bunch of cool benefits, mainly saving energy (and cash) and setting the perfect mood for any occasion. Let’s dive into why dimmable LEDs are pretty awesome:
1. Saving Energy and Money
Imagine if you had a magic trick to cut your electricity bill in half. Well, dimmable LED lights are kind of like that magic trick. When you dim an LED light to 50% brightness, it doesn’t just look half as bright; it actually uses about 50% less energy.
This means if you often enjoy your room a bit less bright, you’re also paying less to light it up. Over time, these savings add up, making dimmable LEDs a smart choice for your wallet and the planet.
2. Setting the Perfect Mood
Lighting can make or break the vibe of a room. Think about it: you wouldn’t want the same bright lights for a cozy movie night that you’d use when you’re reading or cooking. With dimmable LEDs, you can adjust the light to match exactly what you’re doing. Want to relax?
Dim the lights to create a calm, soothing atmosphere. Need to focus on work or a hobby? Brighten them up without switching bulbs or lamps. This flexibility lets you use one room for many different activities, all with the right lighting.

3. Controllability
Dimmable LEDs give you the superpower to adjust your room’s brightness exactly how you want it. Imagine you’re throwing a small dinner party. With dimmable lights, you can turn down the brightness to make the atmosphere cozy and welcoming, perfect for a relaxing evening.
Or, when you need to buckle down and focus on some work or a project, crank up the brightness to help keep your mind alert and sharp. This ability to control the light intensity not only affects the mood but can also help improve your productivity and comfort.
4. Longevity
Here’s a cool fact: dimming your LEDs can actually make them last longer. It’s like running a car at a steady, moderate speed instead of always revving the engine. When you dim LED lights, you reduce the energy flowing through them, which means they don’t work as hard and don’t get as hot.
Heat is one of the main reasons lights wear out, so less heat means a longer life for your LEDs. This is beneficial as it allows you to save time, effort, and money over time by reducing the need for frequent replacements.
Ask For Free Quote
Let us Respond Promptly for your Needs :)
The Advantages of Proper Lighting
Proper lighting does more than just help you see better. It can significantly impact your mood and energy levels. Bright, clear light can invigorate and awaken you, making it easier to concentrate and stay focused.
On the flip side, softer, dimmer light can help you unwind and relax after a busy day. With dimmable LEDs, you have the flexibility to create the perfect lighting for any situation, whether you’re reading, working on a hobby, or just chilling out.
- Boosting Well-being with Brightness: Imagine waking up to a room bathed in gentle, bright light that gradually increases to mimic the natural sunrise. Such an environment doesn’t just help you wake up more naturally; it sets a positive tone for the entire day. Studies have shown that exposure to bright light, especially in the morning, can improve mood and energy levels, making it easier to tackle the day’s challenges with a more upbeat mindset.
- Enhancing Productivity Through Customized Illumination: Consider the scenario of a graphic designer who spends hours on detailed projects. Proper lighting here is not just about having enough light but about having the right type of light. Adjustable LED lighting can provide the perfect balance between brightness and color temperature, reducing eye strain and increasing concentration and accuracy in work.
How to Properly Dim Light Bulbs?
Here’s what you need to know about challenges with LED dimming compatibility, wattage, and load capacity.
1. Understanding Compatibility
One of the main challenges with LED dimming is compatibility. Not all LED bulbs are designed to dim, and not all dimmer switches work with every LED bulb. To avoid issues like flickering, buzzing, or incomplete dimming, it’s crucial to:
- Check Bulb Compatibility: Look for LED bulbs that specifically say they are “dimmable.” This information is usually on the packaging.
- Use the Right Dimmer: Make sure your dimmer switch is compatible with LED technology. Many older dimmer switches are designed for high-wattage incandescent bulbs and may not work well with the lower wattage of LED bulbs.
2. Wattage and Load Capacity
Dimmer switches are designed to handle a specific range of wattages. This is often more of an issue with LEDs because they consume much less power than incandescent bulbs.
- Calculate Total Wattage: Add up the wattage of all the bulbs that the dimmer controls. Ensure this total is within the dimmer’s handling capacity.
- Understand Minimum Load: Some dimmer switches have a minimum load requirement (the smallest amount of wattage they can control). Because LEDs use such low wattage, if the total wattage of the LEDs is below this minimum, the dimmer might not work correctly.

3. Solutions and Tips
- Choose Compatible Products: Manufacturers often provide lists of bulbs and dimmers that work well together. Checking these can save a lot of trouble.
- Consider Smart LED Bulbs: Smart bulbs with built-in dimming capabilities can often bypass these compatibility and load issues since they’re controlled via apps and don’t rely on traditional dimmer switches.
- Trial and Error: Sometimes finding the right bulb and dimmer combination requires a bit of experimentation. Purchasing one bulb and dimmer to test before outfitting your entire home can prevent frustration.
Common problems and troubleshooting tips for dimming light LED bulbs
When you’re adjusting the brightness of your light bulbs with a dimmer, sometimes things don’t go smoothly. Two common problems are “dropping off” and “popping on.” Let’s break down what these are and how you can fix them.
1# Dropping Off
Imagine you’re dimming your lights to create a cozy atmosphere for movie night, but suddenly, the lights turn off completely instead of dimming to the level you wanted. This problem is called “dropping off.”
It usually happens because the dimmer switch and the light bulbs aren’t perfectly matched. Some dimmers have a minimum load (the smallest amount of power they can handle before turning off), and if your light bulbs don’t meet this requirement, the lights might just turn off as you dim them.
How to Fix:
- Check Compatibility: Make sure your light bulbs and dimmer are compatible. Look for bulbs that are specifically labeled as “dimmable.”
- Meet the Minimum Load: If your dimmer has a minimum load, ensure your lighting setup meets or exceeds this. Sometimes adding more bulbs to the circuit or switching to a different type of bulb can help.

2# Popping On
Now, let’s say you’re doing the opposite: you’re trying to make the room brighter in the morning. But instead of gradually getting brighter, the lights suddenly jump to full brightness.
This “popping on” can be quite jarring and is not how a smooth dimming system should work. Like dropping off, this issue often stems from a mismatch between the dimmer and the light bulbs, where the dimmer’s settings or electrical characteristics don’t align well with what the bulbs can handle.
How to Fix:
- Adjust the Dimmer Settings: Some dimmers come with adjustable settings that allow you to set the minimum and maximum light levels. Tweaking these settings might prevent the lights from popping on.
- Switch to Compatible Bulbs: Again, compatibility is key. Ensure your bulbs are designed to work with your dimmer. Some modern LED bulbs are better at handling a wide range of dimming levels without issues.
3# Low Glow
Low glow is when you turn your dimmable lights off, but they still emit a faint, ghostly light instead of going completely dark. This usually happens because of residual electricity in the system.
Even when dimmed to what you think is “off,” some dimmer switches still allow a tiny bit of electricity to pass through, which is enough to make LED bulbs glow faintly.
How to fix it:
- Check Your Dimmer Switch: Not all dimmer switches are fully compatible with all LED bulbs. You might need a switch that’s specifically designed for LEDs.
- Try a Different Brand or Type of Bulb: Some bulbs are more susceptible to low glow than others. Switching brands or types might solve the problem.
- Install a Bleeder: Electricians can install a device known as a “bleeder” to help draw away the residual electricity causing the glow.

4# Flickering/Strobing/Flashing
- Flickering: Rapid, frequent changes in brightness, similar to the flicker of a flame.
- Strobing: Slower, more rhythmic changes in brightness.
- Flashing: Sporadic, unpredictable bursts of light.
These issues can occur for various reasons, including incompatible dimmer switches, poor quality bulbs, or incorrect installation. LED bulbs are particularly sensitive to fluctuations in the electrical current, which can cause these effects.
How to fix them:
- Check Compatibility: Ensure your bulbs and dimmer switches are compatible. Search for dimmers explicitly crafted for LED lighting.
- Quality Matters: Invest in high-quality LED bulbs from reputable manufacturers. They’re less likely to flicker, strobe, or flash when dimmed.
- Proper Installation: Make sure your lighting system is correctly installed. Loose connections can lead to flickering.
- Load Minimums: Some dimmer switches have a minimum load requirement (the total wattage they can handle). If your LED bulbs don’t meet this minimum because they’re so energy-efficient, it can cause issues. Adding more bulbs or switching to a different dimmer can help.
- Electrical Check: Sometimes, the issue is with your home’s electrical system itself, like an overloaded circuit. If the above tips don’t help, it might be time to call in a professional electrician to take a look.
Remember, with a bit of troubleshooting, you can solve most dimming issues and enjoy the mood and energy savings that dimmable LED lights offer.
Ask For Free Quote
Let us Respond Promptly for your Needs :)
Selecting the Right LED Dimmer Switch for Your Needs
The first step in selecting a dimmer is to figure out how many switches control your light fixture. Here’s a breakdown of the four basic dimmer types:
1. Single-Pole Dimmer
This is for light fixtures controlled by one dimmer switch only. Imagine you have a lamp in your living room that’s only operated from one spot – that’s where a single-pole dimmer comes in. It’s the sole switch for turning your lights on, off, and adjusting brightness.
2. Three-way or Four-way Dimmer
These dimmers are made for lighting systems that are managed by a single dimmer along with one or more on/off switches located in various places. For example, if you have a hallway light that you can control from both ends of the hallway, you might use a three-way dimmer. This setup allows for dimming control at one point and basic on/off control at the others.
3. Multi-location Dimmer
If your lighting setup requires control from several different spots, you’ll want to opt for a multi-location dimmer. This allows you to adjust the brightness from several places, providing maximum flexibility. It’s perfect for large rooms or open-plan areas where you might want to control lighting from different spots.

4. Plug-In Dimmer
These dimmers are perfect for table and floor lamps, offering exceptional user-friendliness. You just plug your lamp into the dimmer, and then connect the dimmer to the wall outlet. Most of them are compatible with different bulb types, such as incandescent, CFL, and LED bulbs, providing versatility for temporary or portable lighting arrangements.
5. Bulb Type
- Incandescent/Halogen: If your home has these traditional bulbs, you’ll use standard dimmers designed for them. These dimmers work by quickly switching the bulbs on and off, faster than we can see, to make them seem dimmer.
- Compact Fluorescent (CFL) and LED: First, make sure your CFL or LED bulbs can dim. Nowadays, dimmable LEDs and CFLs are getting better and more common. But, you have to match these bulbs with the right dimmer. An old-school incandescent dimmer won’t work well with LEDs or CFLs, causing them to not dim properly or even mess up.
- Magnetic Low-Voltage (MLV) and Electronic Low-Voltage (ELV): Low-voltage lights use transformers to work right. If the transformer is magnetic, you need a magnetic dimmer. These are good for dimming by managing the power in a specific way. For lights with electronic transformers, you’ll need an electronic dimmer that dims in a different way that matches these transformers.
6. Wattage
Knowing the type of bulb is one thing, but you also need to think about how much power your dimmer can handle. This gets tricky when you switch from high-wattage incandescent bulbs to low-wattage LEDs. You might think you can use a lot more LEDs because they use less power, but it’s not that simple.
For instance, if you have a dimmer that can handle 300 Watts and you used to connect five 60-Watt incandescent bulbs to it, you can’t just switch to thirty 10-Watt LEDs. Even though LEDs use less power, they have something called “inrush current” – a big jolt of power when you first turn them on. So, if your dimmer was good for five old bulbs, stick to about the same number of LEDs to keep things working smoothly.

Conclusion
As we conclude this exploration into the world of LED dimming, it’s important to remember the versatility and efficiency that dimmable LED lights bring into our homes and workplaces. From creating the perfect ambiance with mood lighting to saving on energy bills, the benefits of LED dimming are wide-ranging.
We’ve covered how dimming LEDs works, from the rapid on-and-off switching of pulse width modulation (PWM) to ensuring you have the right type of dimmer, whether it’s a leading edge or trailing edge dimmer, to match your lighting needs.
RC Lighting Helps Illuminate Your Space with Precision
Upgrade to the Perfect LED Dimming Solution! Tired of the one-size-fits-all approach to your home’s lighting? It’s time to switch to a solution that matches every mood and need. Whether you’re basking in the soft glow of dimmable LED lights or seeking the optimal ambiance with advanced LED dimming technology, finding the right LED dimmer is key.
From the cozy corners lit by incandescent bulbs to the vibrant spaces illuminated by LED light bulbs, ensure every room shines its best. Visit us at RC Lighting to learn more about customizing your lighting experience with our dimmable LED lamps and LED dimmers, contact us now!



